 丁香医生审稿专业委员会同行评议通过
丁香医生审稿专业委员会同行评议通过内容
宝宝身上有红疹是怎么回事?怎么办?
1. 可能是湿疹
如果红疹长在身体对称部位、反复出现,多伴有瘙痒、发红、脱屑和结痂,多考虑湿疹。
湿疹尤其在干燥、炎热的环境下加重,如果在接触了某些食物、花粉或者洗涤用品后出现,可能也与过敏有关[1]。
家长如何做[2,3]:
-
最重要的是保湿,用婴儿保湿乳膏或软膏多次涂抹在宝宝皮肤上,尤其在洗澡后立即涂抹有助于缓解症状。
-
避免直接接触可能刺激皮肤的物质,查找并回避过敏原。注意清洁,保持居住环境通风舒适,适当减少衣物,避免宝宝抓挠。
-
在皮疹红肿、渗出严重时,建议及时就医,可以遵医嘱使用小剂量的弱效糖皮质激素类药膏如地奈德软膏等,对缓解瘙痒和红肿很有效果。
高能预警 ↓
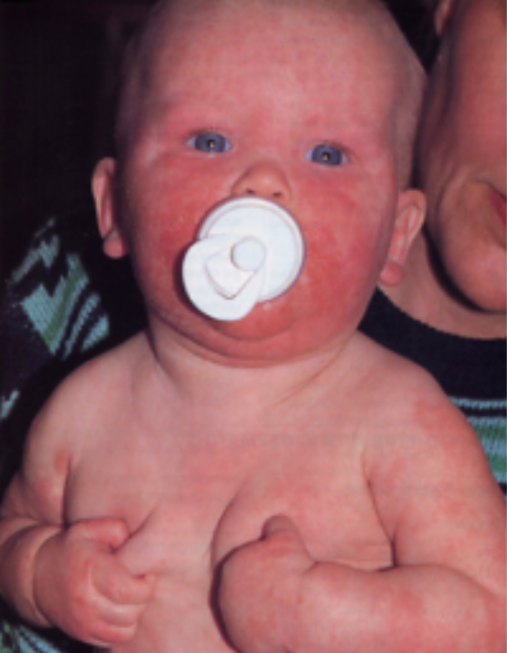
图片来源:[1]2. 可能是尿布疹
如果宝宝屁股上,尤其是尿布覆盖的区域出现了红疹,多考虑尿布疹。
表现:
皮肤上可以见到疙疙瘩瘩的粉红色皮疹,较严重时会见到更广泛的红斑,伴有浸液或浅表糜烂[4,5]。
如果不正规治疗,还可能会合并细菌感染或者真菌感染,这时的皮疹可能会出现脓疱疮或者看起来较硬,表面发亮,像牛肉样的红色斑块[6,7]。
家长如何做[8-10]:
-
治疗和预防尿布疹最好的办法就是保持宝宝臀部清洁和干燥,越接触潮湿的脏尿布时间长,皮疹就可能越严重。
-
已经出现尿布疹的部位,尽量用清水清洗,用棉巾或者棉球蘸干皮肤,等皮肤完全干燥了再使用含凡士林、氧化锌的霜剂涂上。 如果合并了细菌或者真菌感染,还可能需要遵医嘱使用抗生素软膏及抗真菌的药物。
-
如果皮肤特别红,有脓头或者黄色、白色的渗液,局部皮肤发热或者孩子已经发烧,都要及时就诊。
3. 可能是痱子
如果在炎热天气下,宝宝的皮肤上出现了一些细小的疹子,大多在毛孔上方,位于皮肤皱褶处,或者衣物覆盖的地方,多考虑痱子。
表现:
痱子又分为晶痱、红痱和脓痱。晶痱,是透明的小水泡;红痱,是红色的小疙瘩,毛囊周围有发炎;脓痱,就是红痱上面有脓头,这种是感染了的痱子[11,12]。
家长如何做:
-
首先就要保持环境凉爽,空调温度可以调到 24~26℃ 左右,及时调整宝宝衣物,选择透气、轻薄的,保持宝宝皮肤清洁,不要在气温很高的时候出门。
-
痒的部位可以使用低浓度的激素类软膏,包括口服止痒药物在内,都要在医生指导下使用。如果已经合并细菌感染了,还可能需要使用抗生素软膏[13]。
-
如果皮疹量很多,家长护理后仍然没有缓解,瘙痒严重有抓破和感染,建议就诊。
参考资料· Rudikoff D, Lebwohl M. Atopic dermatitis. Lancet 1998; 351:1715.
· van Zuuren EJ, Fedorowicz Z, Christensen R, et al. Emollients and moisturisers for eczema. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017; 2:CD012119.
· Ellis C, Luger T, Abeck D, et al. International Consensus Conference on Atopic Dermatitis II (ICCAD II): clinical update and current treatment strategies. Br J Dermatol 2003; 148 Suppl 63:3.
· Boiko S. Treatment of diaper dermatitis. Dermatol Clin 1999; 17:235.
· Atherton DJ. A review of the pathophysiology, prevention and treatment of irritant diaper dermatitis. Curr Med Res Opin 2004; 20:645.
· Wolf R, Wolf D, Tüzün B, Tüzün Y. Diaper dermatitis. Clin Dermatol 2000; 18:657.
· Weston WL, Lane AT, Weston JA. Diaper dermatitis: current concepts. Pediatrics 1980; 66:532.
· Scheinfeld N. Diaper dermatitis: a review and brief survey of eruptions of the diaper area. Am J Clin Dermatol 2005; 6:273.
· Spraker MK, Gisoldi EM, Siegfried EC, et al. Topical miconazole nitrate ointment in the treatment of diaper dermatitis complicated by candidiasis. Cutis 2006; 77:113.[10]Shin HT. Diaper dermatitis that does not quit. Dermatol Ther 2005; 18:124.[11]Al-Hilo MM, Al-Saedy SJ, Alwan AI. Atypical presentation of miliaria in Iraqi patients attending Al-Kindy Teaching Hospital in Baghdad: A clinical descriptive study. Am J Dermatol Venereol 2012; 1:41.[12]LUBOWE II, PERLMAN HH. Periporitis staphylogenes and other complications of miliaria in infants and children. AMA Arch Derm Syphilol 1954; 69:543.[13]Kirk JF, Wilson BB, Chun W, Cooper PH. Miliaria profunda. J Am Acad Dermatol 1996; 35:854[14]ALSOP J, FLEWETT TH, FOSTER JR. 'Hand-foot-and-mouth disease' in Birmingham in 1959. Br Med J 1960; 2:1708.[15]ROBINSON CR, DOANE FW, RHODES AJ. Report of an outbreak of febrile illness with pharyngeal lesions and exanthem: Toronto, summer 1957; isolation of group A Coxsackie virus. Can Med Assoc J 1958; 79:615.[16]Kaplan AP. Urticaria and angioedema. In: Middleton's Allergy: Principles and practice, 7th, Adkinson NF, Bochner BS, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske RF, Simons FER (Eds), Mosby, St Louis, MO 2009. Vol 2, p.1063.[17]Zuberbier T, Asero R, Bindslev-Jensen C, et al. EAACI/GA(2)LEN/EDF/WAO guideline: management of urticaria. Allergy 2009; 64:1427.[18]JURETIC M. Exanthema subitum a review of 243 cases. Helv Paediatr Acta 1963; 18:80.[19]Clemens HH. Exanthem subitum (roseola infantum): report of 80 cases. J Pediatr 1945; 26:66.[20]Jenista JA. Human herpesvirus-6 and human herpesvirus-7 infections. In: Textbook of Pediatric Care, McInerny TK (Ed), American Academy of Pediatrics, Elk Grove Village, IL 2009.[21]Pimentel de Araujo F, Tinelli M, Battisti A, et al. An outbreak of skin infections in neonates due to a Staphylococcus aureus strain producing the exfoliative toxin A. Infection 2018; 46:49.[22]Liu C, Bayer A, Cosgrove SE, et al. Clinical practice guidelines by the infectious diseases society of america for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in adults and children. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 52:e18.[23]Fortunov RM, Hulten KG, Hammerman WA, et al. Evaluation and treatment of community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus infections in term and late-preterm previously healthy neonates. Pediatrics 2007; 120:937.[24]Berger EM, Orlow SJ, Patel RR, Schaffer JV. Experience with molluscum contagiosum and associated inflammatory reactions in a pediatric dermatology practice: the bump that rashes. Arch Dermatol 2012; 148:1257.[25]Brown J, Janniger CK, Schwartz RA, Silverberg NB. Childhood molluscum contagiosum. Int J Dermatol 2006; 45:93.[26]Straus SE, Ostrove JM, Inchauspé G, et al. NIH conference. Varicella-zoster virus infections. Biology, natural history, treatment, and prevention. Ann Intern Med 1988; 108:221.[27]Heininger U, Seward JF. Varicella. Lancet 2006; 368:1365.[28]American Academy of Pediatrics. Varicella-zoster virus infections. In: Red Book: 2018 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 31st ed, Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, Long SS (Eds), American Academy of Pediatrics, Itasca, IL 2018. p.869.[29]Shulman ST, Bisno AL, Clegg HW, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2012; 55:e86.[30]Powers GF, Boivert PL. Age as a factor in Streptococcosis. J Pediatr 1944; 25:481.[31]Shulman ST, Bisno AL, Clegg HW, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of group A streptococcal pharyngitis: 2012 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2012; 55:1279.[32]Best JM, Icenogle JP, Brown DWG. Rubella. In: Principles and Practices of Clinical Virology, 6th Ed, Zuckerman AJ, Banatvala JE, Schoub BD, et al (Eds), John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, West Sussex, UK 2009. p.561.[33]Cherry J, Baker A.. Rubella virus.. In: Feigin and Cherry's Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 8th ed., Cherry JD, Harrison GJ, Kaplan SL (Eds), Elsevier, Philadelphia 2019. p.1601.[34]American Academy of Pediatrics. Rubella. In: Red Book: 2018 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases, 31st ed, Kimberlin DW, Brady MT, Jackson MA, Long SS (Eds), American Academy of Pediatrics, Itasca, IL 2018. p.705.[35]Morens DM, Anderson LJ, Hurwitz ES. National surveillance of Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 1980; 65:21.[36]Baker AL, Lu M, Minich LL, et al. Associated symptoms in the ten days before diagnosis of Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 2009; 154:592.[37]https://www.uptodate.cn/contents/zh-Hans/rubella?search=%E9%A3%8E%E7%96%B9&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1-
- 就诊

